Iggy operates as an append-only log system, where messages are added without modification or deletion, allowing for a reliable, sequence-oriented data structure.
Unlike other systems, this platform is lightweight and straightforward to configure, making it an attractive option for environments that don't require the complex infrastructure of Kafka or RabbitMQ. This simplicity can reduce deployment costs and the burden on system resources, making it suitable for applications with low-latency requirements or without advanced message durability needs.
System with Kafka or RabbitMQ
Iggy shares key similarities with other messaging systems such as Kafka and RabbitMQ in essential aspects of message streaming and processing. Like Kafka, it enables real-time data streaming through the use of topics and partitions, organizing messages so that consumers can read them efficiently. This also enables parallelization, as messages in different partitions can be processed simultaneously by parallel consumers.
On the other hand, Iggy shares some features with RabbitMQ, such as ease of setup in smaller environments and the ability to offer a lightweight option for applications that don't require massive scalability. Like RabbitMQ, Iggy may be suitable for developers who prefer a lower-complexity messaging system that facilitates rapid deployment in applications that are less dependent on fault tolerance at the distributed network level.
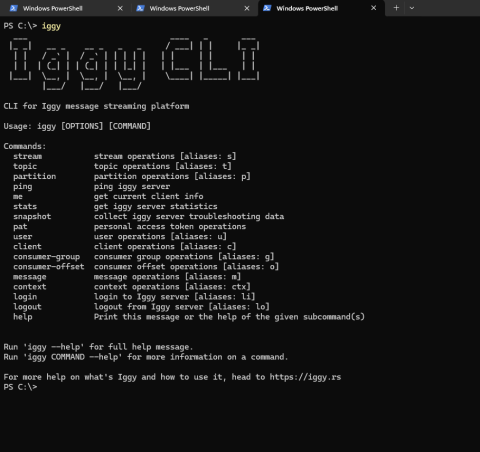
Basic Iggi-CLI Operation
The Iggy CLI allows developers to interact with the server using simple console commands, such as creating streams and topics or sending messages, making it easy to administer and quickly test without additional configuration.
Basic web UI functionality
Iggy has excellent integration with Java thanks to the libraries they've developed. These libraries allow you to perform any operation that can be performed with the aforementioned CLI tool, such as creating a basic producer and consumer, as well as managing your topic and stream.
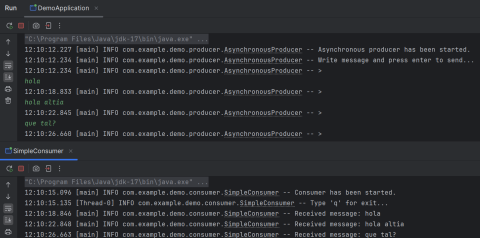
Java producer-consumer operation
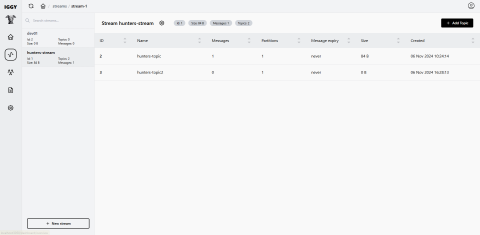
Iggy's user interface (UI) provides a visual way to manage messages and topics, but it is currently under development, which may cause some bugs in some features.
Architecture
Iggy is based on one core concept: the append-only log. This is a data structure that only allows append-only operations, meaning data can only be added to the structure in the order it is received and cannot be deleted or modified once added. This is essential to ensure data immutability and order.
Once this is understood, we can move on to explain the general structure that this platform follows:
- Stream: A logical space where related topics are grouped. It can contain one or more topics. Each stream is identified by an ID.
- Topic: A logical entity that groups messages of a specific type. It is responsible for storing partitions.
- Partition: A partition is where records (messages) are stored and are part of the topics. A partition acts like a simple database, but with append-only operations. The order of records within a partition is guaranteed, but between partitions it is not. Partitions are independent, allowing each partition to be consumed by a different consumer and allowing horizontal scaling.
- Segment: This is a part of the partition. It acts as the actual physical layer where records are stored in binary format, in the form of files.
Iggy vs Kafka performance comparison

In this table we can see that the number of messages sent in Kafka is much higher than in Iggy regardless of the time interval , we can also see that the number of messages sent per second does not increase if the time interval is higher.

In this second table we can see again that Kafka takes less time to send a certain number of messages, this is important since as we see, when it exceeds a certain volume of messages, the use of Iggy is not the most optimal.
As a final conclusion in the performance comparison, it is demonstrated that Kafka has a significantly higher performance than Iggy, as we pointed out in the previous comparison, this is due to its internal structure and how they are designed.
Finally, with this study of the Iggy tool, we can conclude that it is a very interesting tool to use in small or lightweight systems where a large data volume or very low latency is not required. It is ideal due to its ease of configuration and implementation, in addition to its integration with our system and ease of deployment. Remembering that this tool is still under development, it has great potential and many opportunities in the future.
Want to know more about Hunters?
Being a Hunter means accepting the challenge of testing new solutions that deliver differentiated results. Join the Hunters program and become part of a cross-functional group capable of generating and transferring knowledge.
Get ahead of the digital solutions that will drive our growth. Find more information about Hunters on the website.

Francisco Fernández
Software Technician
Altia



