At ALTIA, we've designed several programs to help people finishing their degree or recent graduates get started in the IT sector, combining their talent and passion for technology. One of these programs is Hunters : people who love trends, have an innovative spirit, and contribute to anticipating future challenges. Being part of Hunters means being part of a cross-functional group with the ability to generate and transfer knowledge . We share some of this knowledge through articles on trends and technology, like the one we'll discuss today, Spring Data Flow .
It's a Spring Cloud tool for processing streaming or batch data using scheduled tasks. The idea is to have a series of microservices deployed on a platform (Kubernetes, for example) that form a data processing pipeline.
What are the advantages of using this technology?
Spring Cloud Data Flow is a platform for creating data processing pipelines, developed in Spring Boot under the Spring Cloud platform. It allows, among other things:
- Local deployments for pipeline testing, which can be done as a normal or Dockerized application.
- Cloud deployment in a Kubernetes cluster, using Helm or as an application. It will interact with Kubernetes to manage the deployment of scheduled tasks such as cron jobs, using a Docker registry as the source of images to deploy jobs as containers.
It has a web console that allows viewing and management of pipelines.
Integrates with OAuth security platforms .
It allows integration with CI/CD platforms through its Rest API.
It officially supports Kubernetes and Cloud Foundry platforms, but there are community projects that support OpenShift, Nomad and Apache Mesos .
What is its architecture like?
Spring Cloud Data Flow has two fundamental pillars:
Stream Processing: Used to execute real-time ETL jobs based on task execution within a pipeline where each stage is an independent application and they communicate through events (Kafka or Rabbit).
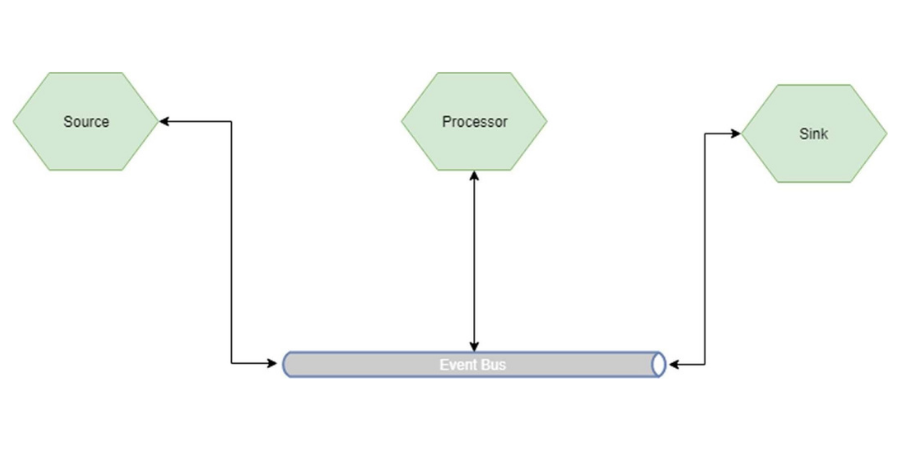
There are three types of nodes:
- Source: Those who react to an event and initiate processing.
- Processor: These are transformations and processing that are done on the event released by the Source.
- Sink: These are final nodes, they receive data from the processors and generate final information.
There are 3 basic entities:
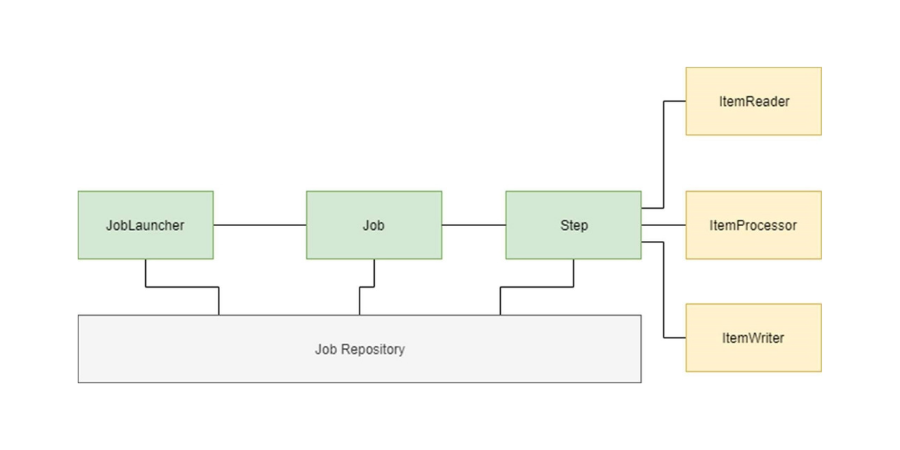
- Task: Short-lived processes that run in microservices.
- Job: Entities that encapsulate a series of steps (at least 1) that constitute the batch processing.
- Step: A domain object that encapsulates a sequential phase within a batch process. Each Step has an ItemReader, an ItemProcessor, and an ItemWriter.
Batch Processing: In this case, the developed microservices must produce execution results for monitoring. These microservices are developed using the Spring Cloud Task and Spring Cloud Batch platforms.
Spring Cloud Data Flow deploys as a microservice , although it has permissions to access the platform where it's deployed, allowing it to execute deployments and schedule jobs. This is possible thanks to the Service Provider Interface module, which includes built-in mechanisms for connecting to Kubernetes and Cloud Foundry.
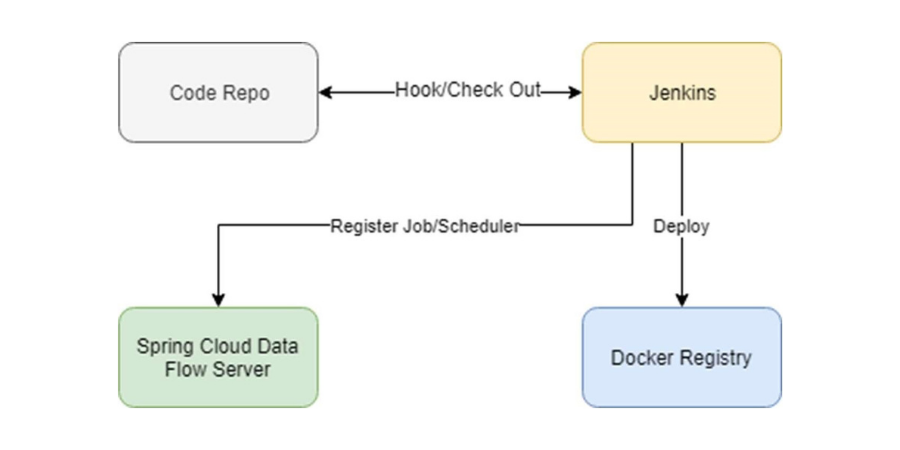
Spring Cloud Data Flow allows integration into Continuous Integration and Deployment workflows thanks to its REST API. The integration scheme would be as follows:
Want to know more about Hunters?
Being a Hunter means accepting the challenge of testing new solutions that deliver differentiated results. Join the Hunters program and become part of a cross-functional group capable of generating and transferring knowledge. Get ahead of the digital solutions that will drive our growth.
Find out more about Hunters .
Solution Architect at Altia




