
Today, the need for data to flow in different formats between heterogeneous systems is an undeniable fact:
- Statistics obtained from clicks on websites where users interact
- Information hidden in emails
- Patterns in images
- Signals sent by sensors that control industrial machinery
Information can come from anywhere, and computer systems must be able to receive that data and process it appropriately so that it can be useful in scenarios such as implementing behavioral patterns, developing AI capable of detecting cancers in images the human eye can't see, or predicting when a machine component may be about to fail.
Information is power, but you have to be able to extract it from data that is not always presented in a simple way.
In Data Engineering, four major blocks of work are distinguished:
- Intake: Data collection from any source
- Transformation: Repairing data into a format that facilitates analysis
- Analysis: Information Extraction
- Storage: Data storage
Apache NiFi
Apache NiFi is an open-source tool designed for automating extract-transform-load (ETL) workflows through visually designed flows. However, the transformations Apache NiFi can perform are not very powerful, but it offers significant capabilities in terms of data ingestion, which is why it is commonly seen integrated into Big Data systems.
In addition, it is capable of working in real time, so it can be integrated into any modern data processing workflow.
Basic components
Flow: The workflow or topology is the definition of the data flow implemented in NiFi and indicates how the data should be managed.
Flowfile: This is the data packet that travels through the flow between processors. It consists of a pointer to the actual data or content (a byte array) and associated metadata called attributes. To speed up system performance, the flowfile does not contain the data itself, but rather points to it in local storage. Many of the operations performed in NiFi do not alter the data itself or require loading it into memory. Specifically, the data is located in the so-called Content Repository.
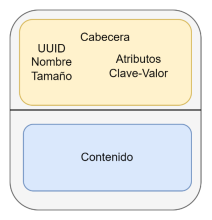
Processor: These are responsible for executing data extraction, transformation, or loading tasks. NiFi allows for various operations to be performed on the processors, as well as for distributing and scheduling their execution. These components also provide an interface for accessing flowfiles and their properties. Apache NiFi has more than 280 processors available, and new ones can be generated through a Java API if necessary.
Connections: These are components that allow any two Processors to interact. They allow flowfiles to be passed between components; in fact, they act as buffers, and they have a backpressure system based on the number of events or disk size. It's also possible to set expiration or priority for flowfiles. Finally, Apache NiFi allows multiple connections to be grouped into one.
Process Group: Grouping of processors and connections to treat them as an independent logical unit within the processing flow. To interact with the rest of the components, they have input and output ports that manage the sending of flowfiles.
Controller Service: Controller services are used to share a resource between different processors . The tool enables seamless connections to external APIs, as well as distributed storage systems such as HDFS, Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage, offering advanced authentication and optimization for handling high-volume requests.
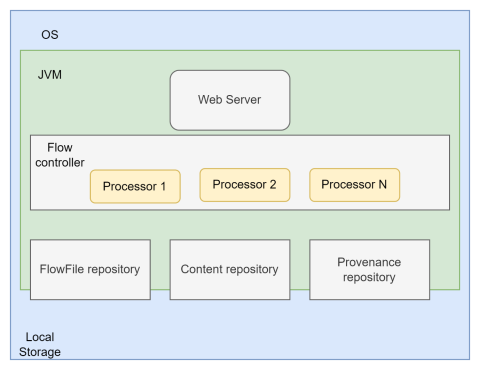
Architecture
The Flowfile Repository stores workflow flowfiles, including both metadata and content pointers. It also stores the current queue. It maintains only the most up-to-date state of the system using the Write-Ahead Log, ensuring that the most up-to-date state can be recovered in the event of a system outage.
The Content Repository stores the contents of flowfiles. Each modification to a flowfile's content is historized, meaning a copy of the current value is made on write before the content is modified. This does not have to be unique in the system and can be divided into sections.
The Provenance repository stores information on the provenance and origin of flowfiles by using snapshots, which allow the lifecycle of each flowfile to be restored. Therefore, this repository adds a time dimension.
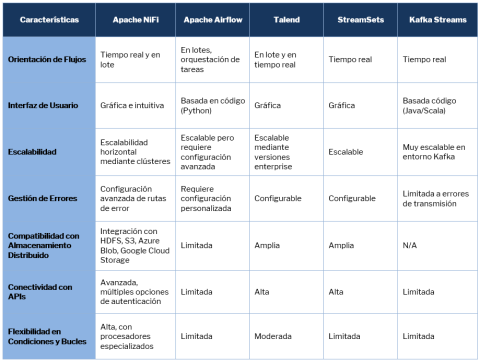
Comparison with other systems
To evaluate Apache NiFi's capabilities in the context of other data integration and processing tools, we can look at a comparison that highlights the key features of each solution, such as their stream orientation (real-time, batch, or both), scalability, error handling, and support for distributed storage and APIs.
Want to know more about Hunters?
Being a Hunter means accepting the challenge of testing new solutions that deliver differentiated results. Join the Hunters program and become part of a cross-functional group capable of generating and transferring knowledge.
Get ahead of the digital solutions that will drive our growth. Find more information about Hunters on the website.

Diego Ríos
Data Engineer
Altia



