
Apache Hop is an open source data orchestration platform that makes it easy to process data by creating pipelines or workflows to perform ETL.
Using this tool, developers can design workflows to work with data visually, allowing them to focus on what task to perform, rather than how to perform it, avoiding writing lines of code.
What features does Apache Hop have?
In Apache Hop, the user designs their flow in the interface. The Hop engine then receives the instructions and executes them via a plugin.
All Hop functionality is integrated through plugins. It natively includes more than 400 plugins that allow you to design pipelines and/or workflows, handle small and large data locally, and execute in different environments (external servers, cloud, clusters, etc.). In addition, Hop natively integrates Apache Beam, which allows you to run jobs in Apache Spark, Apache Flink, or Google Dataflow.
Hop consists of command line tools that offer different actions:
- Hop-gui: Opens the user interface to allow you to create flows, pipelines, manage projects, configurations, and explore features.
- Hop-server: Starts a server to run workflows or pipelines.
- Hop-run : Executes jobs by specifying project configuration, environment and/or properties as parameters.
- Hop-conf: Responsible for managing configuration related to environment variables, projects, executions, and third-party plugins.
- Hop-search: Used to search for metadata within a project directory.
- Hop-import: Allows you to import and convert third-party plugins to Apache Hop format.
- Hop-encrypt: Encrypts plaintext passwords for use in XML files or within various interface components.
Concepts
Hop developers can create workflows and pipelines in Hop GUI. These processes can be executed natively in Hop (local or remote) or on external platforms (Apache Spark or Google Dataflow) using Apache Beam.
The key concepts of Apache Hop are:
Pipelines are collections of transformations, while workflows are a sequence of actions.
Pipelines execute operations that read from different sources (databases, text files, REST services, etc.), process (add, transform, delete rows or columns), and export data in multiple formats. However, workflows are designed to perform chained operations in a specific order.
A transformation is a unit of work performed in a pipeline that operates on data: enrichment, cleansing, filtering, etc. Transformations process data and generate an output that is the input to the next transformation within a pipeline. Typically, transformations within a pipeline run in parallel.
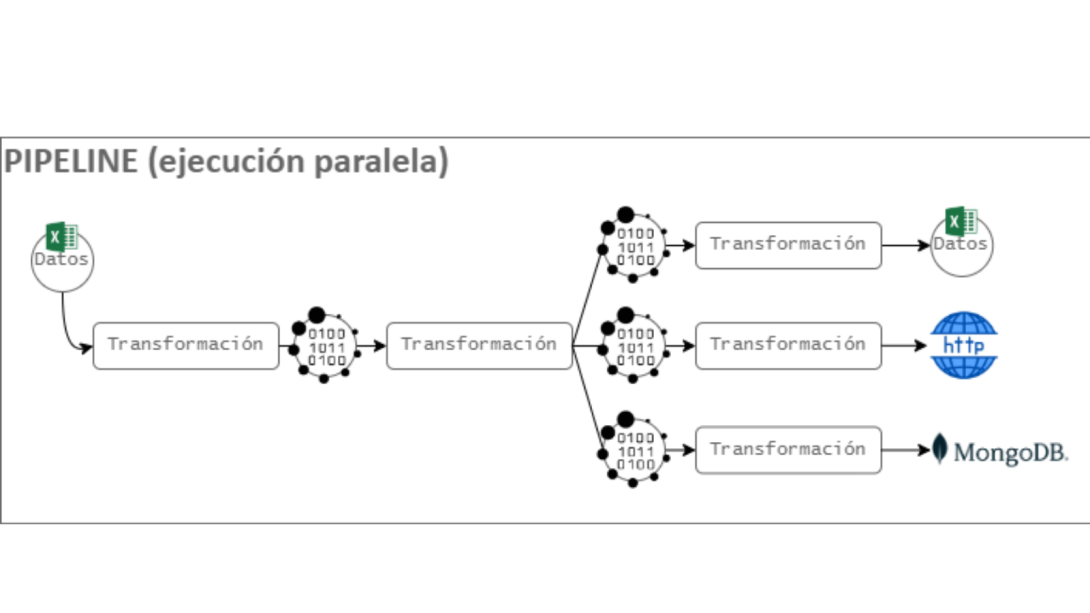
Figure 1: Reading and operations of an Excel file.
In the example in Figure 1, the Excel file is read. A transformation (filter or switch) is then applied to obtain different sections of data. Different operations are then performed on each output: export to an Excel file, post to an HTTP server, and save to MongoDB.
An action is an operation performed in a workflow. It returns a True or False result code that can be used to control the workflow. Actions within a workflow typically execute sequentially, with the option of parallel execution.
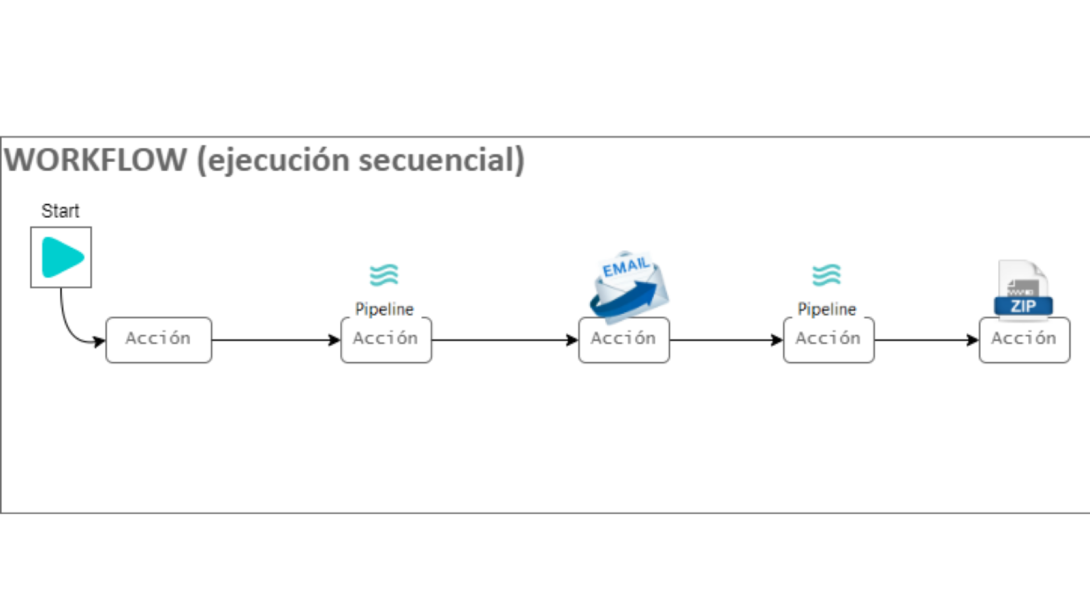
Figure 2: Sequence of pipes, sending mail and encapsulating data in a ZIP.
The example in Figure 2 shows a sequence of actions: running pipelines, sending email, or encapsulating data in a zip.
Projects are a grouping of pipelines, workflows, metadata, variables, and configurations. Within the same project, configurations are separated by environments. By default, we find the different environments: development, testing, production.
What does Apache Hop allow?
Apache Hop, in addition to running simple jobs using pipelines or workflows, allows you to:
- Loading and processing big data by leveraging cloud environments and parallel processing.
- Population of databases to conduct studies with other tools.
- Data migration between applications or between relational and non-relational databases.
- Data profiling and cleaning.
Comparison with Pentaho Data Integration and Spring Cloud Data Flow
Pentaho Data Integration
Apache Hop shares conceptual similarities with Pentaho Data Integration. However, Pentaho doesn't have a project concept, so you can't create environment variables or scripts to configure projects. Shared objects (metadata and configurations) in Pentaho are defined in a shared.xml file, whereas in Hop they are divided into subfolders within the project, which improves structuring and facilitates configuration debugging.
The Apache Hop engine allows jobs to be run externally using Apache Beam, which is not possible in Pentaho.
Hop was born in 2019 as a fork of Pentaho Data Integration, but evolved into projects with different goals and priorities. By sharing a branch with Pentaho, Hop allows you to import jobs, transformations, properties, or database configurations from Pentaho Data Integration.
The main difference between the two is that only Hop allows you to manage projects and environment settings from the interface itself, as well as search for information within a project or configuration. Furthermore, Hop allows you to configure and run functionality through both the command line and the interface, which in Pentaho can only be done through the interface.
In terms of code, Apache Hop is more optimized than Pentaho Data Integration, which has advantages such as:
- Consumption of fewer resources.
- Reduction in loading and execution times.
- Ease of deployment within a Docker container.
Spring Cloud Data Flow
Spring Cloud Data Flow is a tool for building microservices-based streaming or batch data processing pipelines.
Like Apache Hop, it allows for local deployments within a Docker container or Kubernetes cluster. SCDF offers a web console for viewing and managing pipelines.
SCDF presents two types of processing:
- Stream: Execution of tasks within a pipeline that communicate through events. This concept is similar to Apache Hop pipelines, where operations are performed on data through transformations.
- In batches: Microservices performing ETL print the log output to a file for monitoring.
We've got a demo of Apache Hop in this video!
Want to know more about Hunters?
Being a Hunter means accepting the challenge of testing new solutions that deliver differentiated results. Join the Hunters program and become part of a cross-functional group capable of generating and transferring knowledge. Get ahead of the digital solutions that will drive our growth. Find more information about Hunters on the website. Tahir Farooq - Software Technician at Altia
Tahir Farooq - Software Technician at Altia



