
Have you ever had to perform a simple task that cost you more time than you expected? This happens regularly. Searching for a list of clients or invoices, sending an email, or searching for information in a remote repository are some of the problems you have to deal with at unexpected times, and you've probably wished you could do them without interrupting your tasks. Fortunately, we have a tool based on generative artificial intelligence that will help solve these problems in the simplest way possible.
What is Generative AI?
In recent years, there has been tremendous progress and an increase in advanced artificial intelligence models in many fields. Today, you can generate text, audio, images, and even video in just a few seconds, something that seemed unthinkable a few years ago. All of these artificial intelligence tools belong to a specific group: generative AI.
Generative AI is responsible for creating new ideas and content by learning from existing content . All AIs focus on learning to imitate human intelligence, but this one is dedicated to solving new problems and creating results based on the information at its disposal . It is very useful in many fields, but especially as a support for professionals , helping them solve simple and tedious tasks in less time and with less effort .
Numerous systems have been created for this purpose, but today we'll focus on one of great interest regarding the creation of chatbots that can answer specific questions with varying degrees of specialization.
Start-up
This tool is extremely useful for users and customers, but what would happen if we focused on using it to solve real problems and not just offer solutions? With this in mind, we worked to create a prototype that would demonstrate the potential of using a tool like this.
Our program consists of a chatbot accessible through WhatsApp, specialized in solving basic problems with minimal user intervention and using natural language.
Due to the need to incorporate artificial intelligence, the first step is to select one of the conversational AIs currently available and use its API to connect to our program. We looked for free open-source alternatives that didn't limit message sending and settled on Ollama (Open Language Learning for Machine Autonomy), a tool that allows us to run large language models (LLM) in a local environment. This not only allows us to run a working language model in a Kubernetes pod, but since Ollama is a platform for running models, not a model itself, we can switch between the many language models it offers and adapt it depending on the type of response the user needs.
On the other hand, to be able to use WhatsApp as a means of communication, we had to obtain a digital sandbox number that would allow us to add a bot. We achieved this with Twilio, a platform created to facilitate the connection of applications, and primarily chatbots, to WhatsApp.
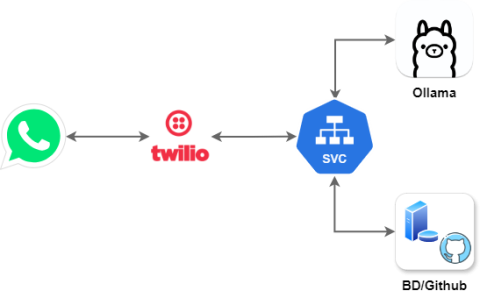
Our application flow would work as shown in the image above. From WhatsApp, we consume the user's messages, which will be processed by Twilio and collected through its API by our Java SVC.
From here, this message will be sent to Ollama's generative AI along with contextual data to facilitate response accuracy. Once obtained, it is returned to our Java SVC, which will use it to connect and process the generated instruction in the relevant service (in our case, a database or GitHub, but it could be any application that allows API communication).
Our application flow would work as shown in the image above. From WhatsApp, we consume the user's messages, which will be processed by Twilio and collected through its API by our Java SVC.
From here, this message will be sent to Ollama's generative AI along with contextual data to facilitate response accuracy. Once obtained, it is returned to our Java SVC, which will use it to connect and process the generated instruction in the relevant service (in our case, a database or GitHub, but it could be any application that allows API communication).
In short, our application translates the user's natural language into the language needed to consume a service's API. Below are two examples of its use:
Working with databases
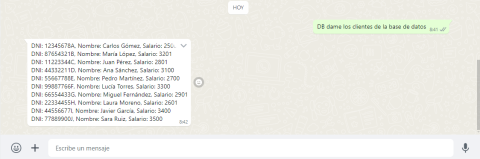
One of the functionalities we've implemented is providing precise solutions to database problems. Based on the user's command, our program will pass the request to the AI, along with the context that allows it to respond appropriately (usually by providing database queries). Once received, the program uses the response to access the user's database and make changes or queries, which it then passes on to the user. This allows database functions to be performed without having to access the database and write code. Furthermore, by making these queries from the program and not directly from the AI, we avoid any type of violation of data confidentiality.
Working with GitHub
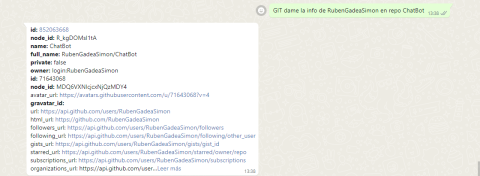
Similarly, we can work with GitHub by making queries and changes without having to access the application itself. The operation is the same: the user sends a request in natural language, and the AI responds in a way that the GitHub API can understand, thus obtaining the results that will ultimately be returned to the user.
Future extensions:
- Integration with other platforms: Incorporate the bot into Telegram, Slack, and Microsoft Teams, allowing users to access its features from different communication and collaboration platforms.
- Training the model to improve its optimization: This allows the AI's responses to be used to access other services and obtain data or make modifications without the user having to access them directly.
- Workflow Automation: Extend capabilities to automate repetitive tasks across services like Docker, Kubernetes, and CI/CD, enabling developers to execute deployments and processes more easily.
- Multilingual Support: Add support for multiple languages to make the bot more accessible to international users.
- Enhanced security: The app will scan the phone number from the received message and identify the associated user. After this, it will check whether the user has permission to access the app.
- New language models: Expand the repertoire with specialized infrastructure and DevOps models to cover more technical areas and improve specialization.
- IoT: The bot can be used to control lights, thermostats, security cameras, and other connected devices directly from WhatsApp. This way, the bot would act as a smart assistant similar to Alexa, facilitating home automation and monitoring work environments from the chat itself.
Support for more databases: To offer a wider range of options and responses, our SVC should ideally be able to process requests to different types of databases in addition to PostgreSQL.
Conclusions
As we've seen, there's great potential in combining a chatbot with generative artificial intelligence. Not only does it serve to answer questions in a broad and natural way, but it can also be specialized and configured with other applications, potentially becoming an essential tool for today's professionals and other users. Our program is just a prototype intended to demonstrate the great capabilities of this approach, but the amount of customization and extension to meet all kinds of needs is practically endless.
Want to know more about Hunters?
Being a Hunter means accepting the challenge of testing new solutions that deliver differentiated results. Join the Hunters program and become part of a cross-functional group capable of generating and transferring knowledge.
Get ahead of the digital solutions that will drive our growth. Find more information about Hunters on the website.





